What Is Personal Finance? A Complete Beginner’s Guide for 2026
In today's fast-paced world, managing money can feel overwhelming. With rising costs for everything from groceries to housing, and economic uncertainties like inflation or job changes, many people struggle to make ends meet. You might find yourself wondering why your paycheck disappears so quickly or how to prepare for big life events like buying a home or retiring comfortably. This is where personal finance comes in—it's the foundation of money management that helps you take control of your income, expenses, and future.
Personal finance is essentially the art and science of handling your money wisely. It covers everything from creating a simple budget to building wealth through smart investing. Whether you're a student just starting out, a young professional dealing with student loans, or someone in mid-career planning for retirement, understanding personal finance basics can transform your financial life. It's not about being rich; it's about making informed decisions to achieve stability and freedom.
This complete beginner’s guide for 2026 will break it all down in simple terms. We'll explore the personal finance definition, why it's crucial, and the key components like budgeting, saving money, investing basics, and debt management. You'll get practical personal finance tips, strategies for effective personal finance planning, and even examples tailored for beginners. By the end, you'll have the tools to improve your personal finance skills and set achievable personal finance goals. No jargon-heavy lectures—just straightforward advice based on proven principles from top financial experts.
Think about it: In 2026, with tools like budgeting apps and online resources at your fingertips, there's never been a better time to master managing personal finance. Poor financial habits can lead to stress, debt piles, and missed opportunities, but good ones build security and open doors. This guide promises to answer all your questions, from "what is personal finance and why is it important" to "how to manage personal finance effectively." Let's dive in and turn your money worries into confident steps forward.
Table of Contents
- What Is Personal Finance?
- Why Is Personal Finance Important?
- Key Components of Personal Finance
- Personal Finance Basics for Beginners
- How to Manage Your Personal Finance Effectively
- Personal Finance Tips and Strategies
- Personal Finance Examples
- Personal Finance Goals
- How to Improve Your Personal Finance Skills
- FAQ
What Is Personal Finance?
Personal finance is the process of planning and managing your money to meet your needs today while building for tomorrow. At its core, it's about making smart choices with your income, expenses, savings, investments, and protections against risks. Unlike business finance, which focuses on companies, personal finance is all about individuals or families handling their own resources.
In simple terms, personal finance management involves tracking where your money comes from and where it goes, then using that info to create a balanced plan. It includes everyday tasks like paying bills and bigger-picture stuff like saving for retirement. Financial literacy—the knowledge to make these decisions wisely—is a big part of it. Without it, people often end up in debt or living paycheck to paycheck.
Experts break it down into five main areas: income (what you earn), spending (what you buy), saving (what you keep), investing (growing your money), and protection (safeguarding it all). But it's not just numbers—it's about behavior too. As one source notes, personal finance is 80% habits and 20% knowledge. Mastering it means gaining control over your life, reducing stress, and achieving goals like financial independence.
Why Is Personal Finance Important?
Personal finance is vital because it directly shapes your quality of life. In 2026, with household debt hitting record highs—over $18 trillion in the US alone—poor money habits can lead to overwhelming stress, limited opportunities, and even health issues. On the flip side, good personal finance planning builds security, freedom, and peace of mind.
First, it helps you meet short-term needs, like covering emergencies without going into debt. An emergency fund can prevent small problems from becoming big ones. Long-term, it's key for goals like retirement or buying a home. With life expectancy rising and medical costs soaring, planning ahead ensures you don't outlive your savings.
It also empowers informed decisions. Understanding financial literacy means avoiding pitfalls like high-interest debt or bad investments. Plus, in an era of job automation and economic shifts, personal finance skills help you adapt—whether by diversifying income or building wealth through investing basics.
Ultimately, it's about independence. Managing personal finance effectively reduces reliance on others and lets you live on your terms, from enjoying hobbies to supporting family.

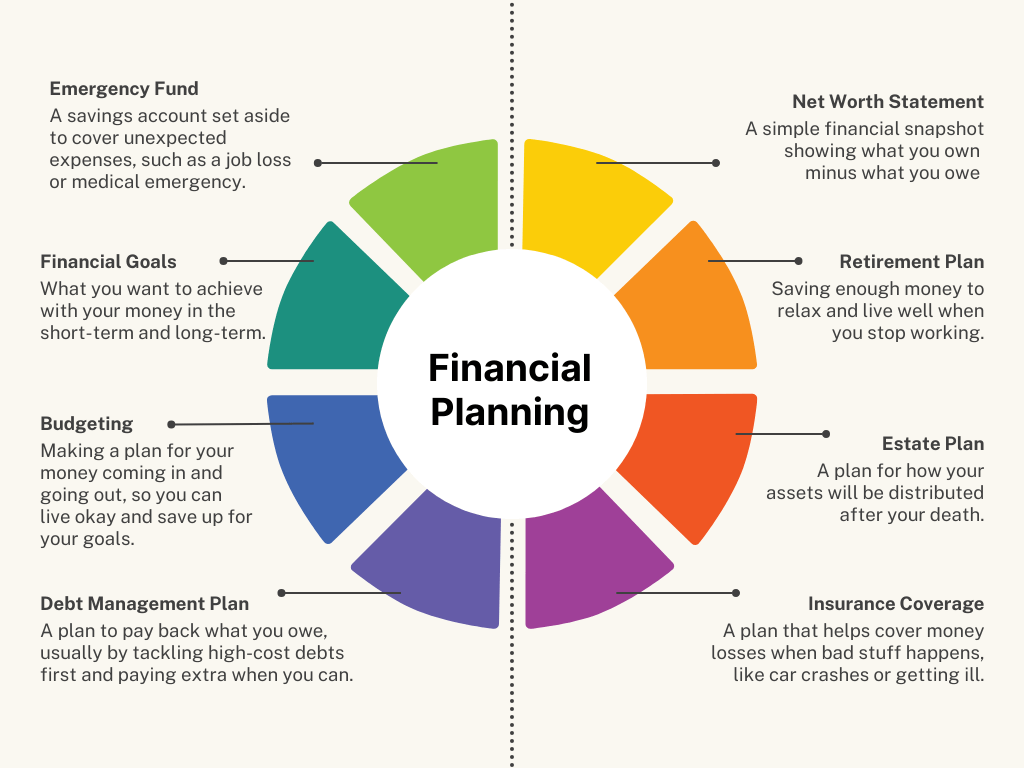
Key Components of Personal Finance
Personal finance has several interconnected parts that work together for overall stability. Here's a breakdown:
Income
Income is the foundation—it's all the money coming in, like salaries, wages, bonuses, dividends, or side gigs. Track your after-tax take-home pay to know what you really have to work with. Boost it by negotiating raises or starting a hustle.
Spending and Budgeting
Spending is where money goes out, on essentials like rent and food, or wants like entertainment. Budgeting ties it together: a plan to allocate income so expenses don't exceed earnings. Use the 50/30/20 rule—50% needs, 30% wants, 20% savings/debt.
| Budget Category |
Percentage |
Examples |
| Needs |
50% |
Rent, utilities, groceries |
| Wants |
30% |
Dining out, hobbies |
| Savings/Debt |
20% |
Emergency fund, loan payments |
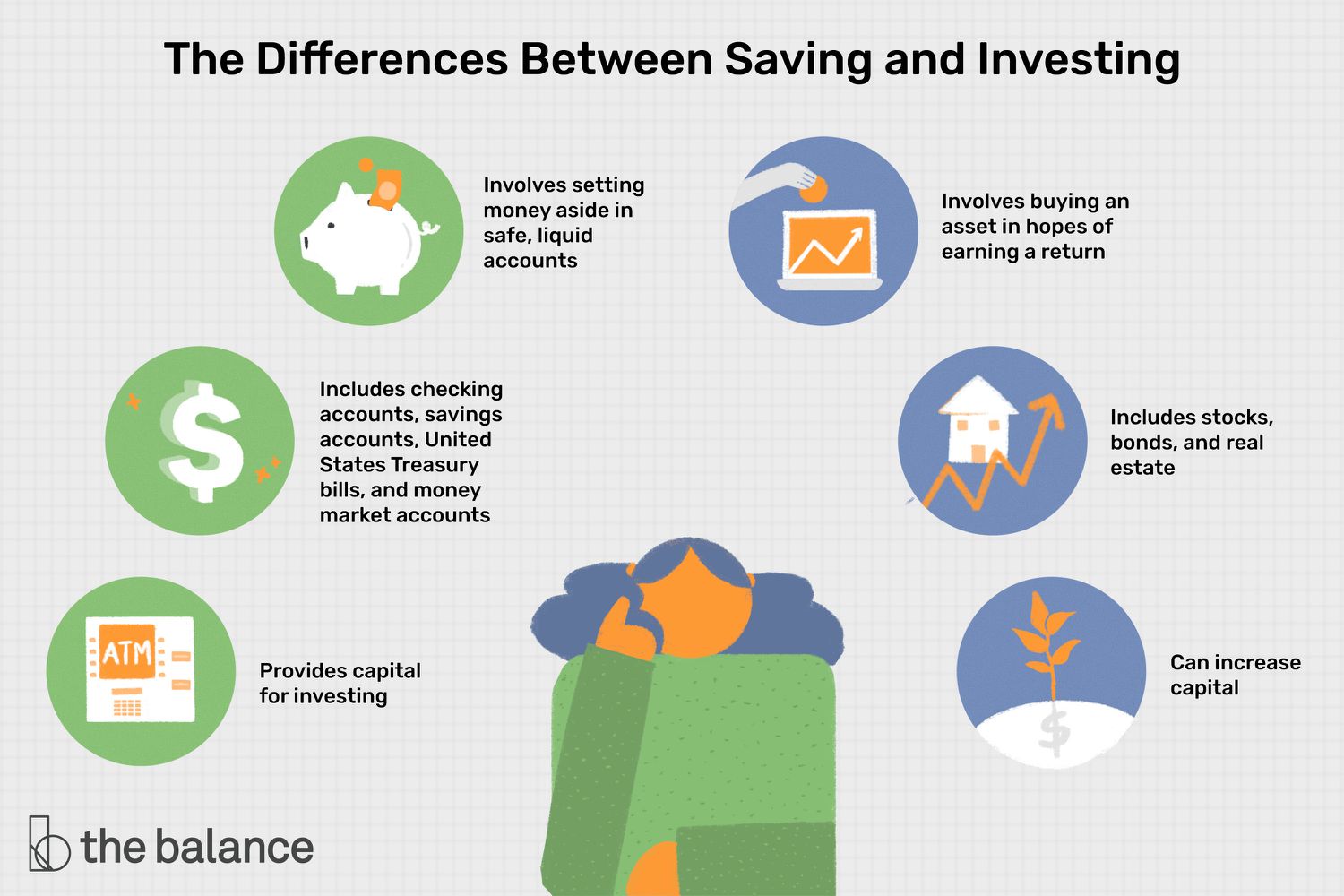
Saving
Saving means setting aside cash for future use, ideally in high-yield accounts. Aim for 3-6 months of expenses in an emergency fund to handle surprises like job loss.
Investing
Investing grows your money by buying assets like stocks, bonds, or mutual funds. Start with retirement accounts like 401(k)s for tax perks. Remember, it involves risk—diversify to balance it.
Protection and Insurance
Protection safeguards against risks with insurance (health, life, auto) and estate planning. It prevents one event from derailing your finances.
Debt Management
Debt is borrowed money, like loans or credit cards. Manage it by prioritizing high-interest ones and avoiding new debt. Good debt (e.g., mortgage) can build wealth; bad debt (e.g., credit cards for luxuries) drains it.
Personal Finance Basics for Beginners
If you're new to this, start small. Personal finance for beginners means learning the ropes without overwhelm. Focus on tracking income and expenses for a month using an app like Mint or Excel. Understand needs vs. wants—needs are essentials, wants are extras.
Build habits: Pay bills on time to boost your credit score, which affects loans and rates. Open a savings account and automate transfers. For students, personal finance might mean managing allowances or part-time jobs while avoiding credit card traps.
Key rule: Live below your means. If you earn $4,000 monthly, spend $3,000 max, saving the rest. Read free resources or take online courses for financial literacy basics.
How to Manage Your Personal Finance Effectively
Effective management follows a step-by-step process. Here's how:
- Assess Your Situation: Calculate net worth (assets minus liabilities) and cash flow (income minus expenses).
- Set Goals: Define short-term (e.g., emergency fund) and long-term (e.g., retirement).
- Create a Budget: Use tools to track and adjust spending.
- Build Savings and Pay Debt: Automate savings; use debt snowball (smallest debts first) or avalanche (highest interest first).
- Invest Wisely: Start with employer-matched 401(k), then IRAs.
- Protect Yourself: Get insurance and make a will.
- Review Regularly: Check quarterly and adjust for changes like raises.
For personal finance for students, prioritize low-cost living and scholarships to minimize loans.
Personal Finance Tips and Strategies
Here are actionable personal finance tips:
✅ Pay yourself first—save 20% of income before spending.
✅ Use cash for discretionary buys to curb impulses.
✅ Diversify income with side gigs.
❌ Avoid lifestyle inflation—don't spend more just because you earn more.
Strategies include the envelope system for budgeting (cash in envelopes for categories) and investing in low-cost index funds for beginners. For debt, consolidate high-rate loans.
| Strategy |
Pros |
Cons |
| Debt Snowball |
Motivational quick wins |
May cost more in interest |
| Debt Avalanche |
Saves on interest |
Slower visible progress |
| 50/30/20 Budget |
Simple balance |
Less detailed for complex finances |
Link to our guide on How to Improve Credit Score for more on debt.
Personal Finance Examples
Real-world personal finance examples make it relatable. Take Sarah, a 25-year-old teacher earning $50,000 yearly. She budgets $2,000 for needs (rent, food), $1,200 for wants, and $800 for savings/debt. By cutting dining out, she pays off $5,000 credit card debt in a year using the snowball method.
For students: Alex, in college, tracks $1,000 monthly from jobs/allowances. He saves $200 for emergencies and invests $50 in a Roth IRA early for compound growth.
In retirement planning, a couple in their 40s invests 15% of income in diversified funds, aiming for $1 million by 65.
Personal Finance Goals
Set SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound). Examples:
- Short-term: Build $1,000 emergency fund in 3 months.
- Medium-term: Pay off $10,000 student loans in 2 years.
- Long-term: Save $500,000 for retirement by age 60.
Align goals with life stages—students focus on debt avoidance, families on education funds. Track progress monthly.
How to Improve Your Personal Finance Skills
Improving skills starts with education. Read books like "The Total Money Makeover" or take free courses on Khan Academy. Practice by reviewing bank statements weekly.
Join communities or use apps for accountability. Consult a financial advisor for personalized plans. Over time, build habits like negotiating bills or learning investing basics through simulations.
Link to Personal Finance for Beginners Guide for more resources.
FAQ
What is personal finance and why is it important?
Personal finance is managing your money through budgeting, saving, and investing to achieve goals. It's important for stability and reducing stress.
How to manage personal finance effectively?
Assess your finances, budget, save first, pay debt, invest, and review regularly.
What are the components of personal finance?
Income, spending, saving, investing, protection, and debt management.
Personal finance tips for beginners?
Track expenses, build an emergency fund, avoid bad debt, and automate savings.
How to improve personal finance skills?
Educate yourself with resources, practice habits, and seek advice.
What are some personal finance goals?
Examples include debt payoff, emergency savings, and retirement funds.
Personal finance examples for students?
Manage allowances by budgeting for needs first and saving small amounts.
How does financial literacy help?
It empowers better decisions for long-term success.
Conclusion
Personal finance is your roadmap to financial freedom in 2026 and beyond. From understanding the basics like budgeting and saving money to advanced strategies in investing and debt management, this guide covers it all. Remember, it's about consistent habits—start small, track progress, and adjust as needed.
Now that you know what personal finance is, take action: Create your first budget today or build that emergency fund. For more, check our related articles like How to Choose the Best Credit Card in 2026 or subscribe to our newsletter for monthly tips. Your future self will thank you.
This article is for educational purposes only. See our Financial Disclaimer.
About author person.